2. Introduction
2.1 Nepal Clearing House Limited (NCHL)
Nepal Clearing House Limited (hereinafter referred to as ‘NCHL’) is a public limited company established under the leadership of Nepal Rastra Bank (the Central bank of Nepal), banks & financial institutions with an objective of establishing national electronic payment, clearing and settlement systems in Nepal.
NCHL has successfully implemented electronic image-based cheque clearing (NCHL-ECC) system; interbank payment system (NCHL-IPS) as automated clearing house; connectIPS system as faster payment system; National payments interface (NPI) as consolidated APIs for payment initiation/ process; and connectRTGS as integration for RTGS transaction initiation. and all the systems are implemented on (T+0) settlement basis and has participation of over 51 banks & financial institutions (BFIs) as direct members and over 30 institutions as indirect/ technical members.
Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) has mandated NCHL to establish additional infrastructure for the establishment and operation of National Payment Switch (NPS) that includes interoperability of card- based transactions (hereinafter referred to as “NPS National Card Switch” or “NPS-NCS”); rollout domestic card scheme for Nepal (hereinafter referred to as “Nepal Payment Card” or “NEPALPAY”); and scale-up of the existing payment systems/platforms to enable non-card based interoperability (hereinafter referred to a ‘non-card Retail System” or “NPS-NPI”). These will together be referred as “National Payment Switch” or “NPS”.
As a part of the National Card Switch, ‘NCHL’ will collect transactions from a trusted source (an acquirer) and deliver it to a trusted destination (an issuer). The trusted destination will use this information to validate the transaction to the cardholder’s account and further authenticate the transaction back to the trusted source through ‘NCHL’. ‘NCHL’ further facilitates the process of clearing a valid authenticated transaction and provides the settlement service. A settlement service is a facility within which funds are exchanged between members to settle transactions and fee amounts. The NPS Card Switching Service will facilitate ATM, POS and eCommerce transactions among all member banks / third party processors (hereinafter referred to as “TPP”) participating in the ‘NCHL’. The NCHL operates on a continuous basis, ensuring that cardholders in Nepal can use their card anytime and that Acquirers and Issuers in Nepal always have access to National Payment Switch.
2.2 NPS National Card Switch (NPS-NCS)
NPS National Card Switch (NPS-NCS) simplifies the current card payment system in Nepal by interconnecting all the switches operated by the banks and payment processors with standard international protocol. It will route the domestic transactions of the locally issued cards either through bank switch or third part processor/ service provider switch to the central switch and for the settlement. The switch also facilitates participating members to issue domestic EMV based card (NEPALPAY) and be interfaced with associated international network (Discover Global Network - DGN). Settlement of the transactions will be carried on central bank money through RTGS, however a separate arrangement (guarantee fund) will mitigate settlement risk on NPS card transactions. The figure below illustrates the simplified scope; the associated components/entities are outlined in the following sections
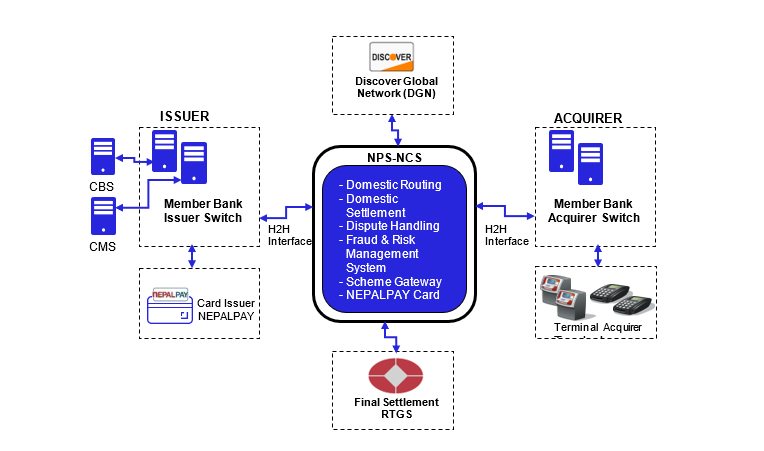
Figure 1: Scope of NPS National Card Switch (NPS-NCS)
2.2.1 NPS National Card Switch (NPS-NCS)
National Payment Switch (NPS) is the interoperable national switch for routing and settlement of domestic transactions. The objectives of NPS are to establish interoperable switch for card transactions, introduce national payments scheme for domestic cards and upgrade the retail payment switch/ system to enhance interoperability of non-card retail transactions.
2.2.2 Issuer
An "issuer" refers to a financial institution or organization that issues payment cards to consumers and businesses. These payment cards can include debit cards, credit cards, prepaid cards, and virtual cards, which are branded with the logo of the NEPALPAY and are typically used for electronic payment transactions.
2.2.3 Acquirer
An "acquirer" refers to a financial institution or entity managing payment card accepting terminals such as ATM, POS, eCommerce that acts as an intermediary between merchants (businesses or service providers) and the payment card system. Acquirers play a crucial role in facilitating electronic payment card transactions.
2.2.4 NEPLPAY EMV Card
National EMV card scheme, NEPALPAY, has been introduced within the framework of the National Payment Switch (NPS), overseen by the Nepal Clearing House Limited (NCHL). This system facilitates the issuance and acquisition of domestic cards, managed either by participating financial institutions or third-party processors operating within Nepal.
2.2.5 International Network
An "International Network" typically refers to a global or international payment card network or association. Discover Global Network (DGN) is the international network for NEPALPAY that facilitates and govern the use of payment cards, including credit, prepaid and debit cards, on an international scale. DGN plays a significant role in enabling cross-border transactions and ensuring the interoperability of payment cards globally.
2.2.6 Settlement
A "settlement" refers to the final and critical phase of a payment card transaction process. It involves the exchange of funds between the issuing bank (the cardholder's bank) and the acquiring bank (the merchant's bank) to complete the transaction. Settlement is a fundamental function in the payment card ecosystem, ensuring that funds are transferred accurately and efficiently. NPS-NCS uses Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system managed by Nepal Rastra Bank for estimated T+0 or T+1 settlement pattern.
2.2.7 Dispute
A "dispute" transaction refers to a payment card transaction for which there is a disagreement or contention between the cardholder and the merchant, typically related to the validity, accuracy, or fairness of the transaction. Disputed transactions are a common aspect of the payment card ecosystem and can arise for various reasons, such as billing errors, unauthorized charges, or disputes over the quality of goods or services received. NPS-NCS provides the centralized dispute portal to participating members for domestic transactions dispute and chargeback purposes.
2.3 Dual Message System and Clearing – Domestic Transactions
Dual Message System (DMS) is a transaction mode where the Acquirer first submits an authorization request to the Issuer, and then submits settlement information to the Issuer collectively in the form of presentment file sometime afterwards. All the international transactions along with domestic POS and eCommerce transactions are managed through DMS. DMS comprises of authorization, clearing and Settlement and uses following exchange of transaction messages:
The card-issuing bank promptly communicates the availability of funds to both the acquirer and the merchant, accompanied by the issuance of an authorization code, ensuring a seamless and secure transaction for the cardholder.
Funds are efficiently claimed from member parties through the NCHL network, facilitated by the exchange of clearing files, streamlining the clearing process with accuracy and transparency.
Members seamlessly exchange funds for the net value of the monetary transactions cleared during the specific processing day, ensuring efficient and accurate financial settlements within the network.
Transaction flow in DMS environment is as follows:
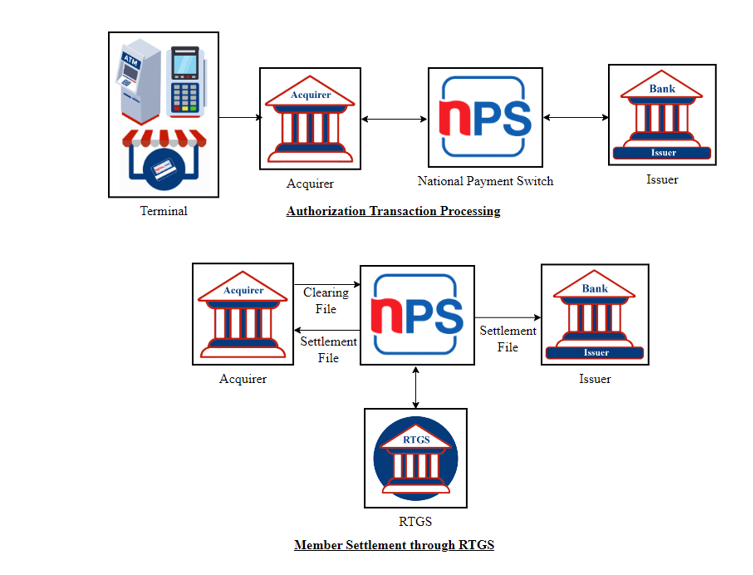
Figure 2: DMS Transaction Flow
2.3.1 Authorization
Authorization is the consent given by an issuer participant (or a third party acting on behalf of that participant) in order to transfer funds. That means an authorization is the process where the issuer bank notifies the acquirer and the merchant of the availability of funds for a cardholder, and issues an authorization code for the transaction.
2.3.2 Clearing
Clearing is the process of transmitting, reconciling and, in some cases, confirming transactions prior to settlement, potentially including the netting of transactions and the establishment of final positions for settlement. The net transaction funds are claimed from member participants using the NPS by exchanging clearing files. Clearing activities facilitate the settlement process.
2.3.3 Settlement
Settlement is the whole process of calculating and submitting the net amount of transaction data based on clearing result for the specific processing day, and completing the fund transfer between member participants.
2.4 Dual Message System and Clearing – International Transactions
In the case of international transactions acquired in NPS Network, acquirer member first submits an authorization request to NPS Card Switch, and then NPS Card Switch submits this authorization request to International Scheme Network. All the international transactions are handled through DMS as following the below scenario:
The card-issuing bank promptly responds the availability of funds to both the acquirer and the merchant through international scheme network and NPS Card Switch, accompanied by the issuance of an authorization code.
Funds are efficiently claimed from acquirer members through the NPS Network using NPS Card Switch Clearing Specification, which will be provided to international scheme network accompanying their particular specification.
Based on the settlement file received from international scheme network, NCHL settles for the net value of the monetary transactions cleared during the specific processing day through RTGS.
Transaction flow in DMS environment is as follows:
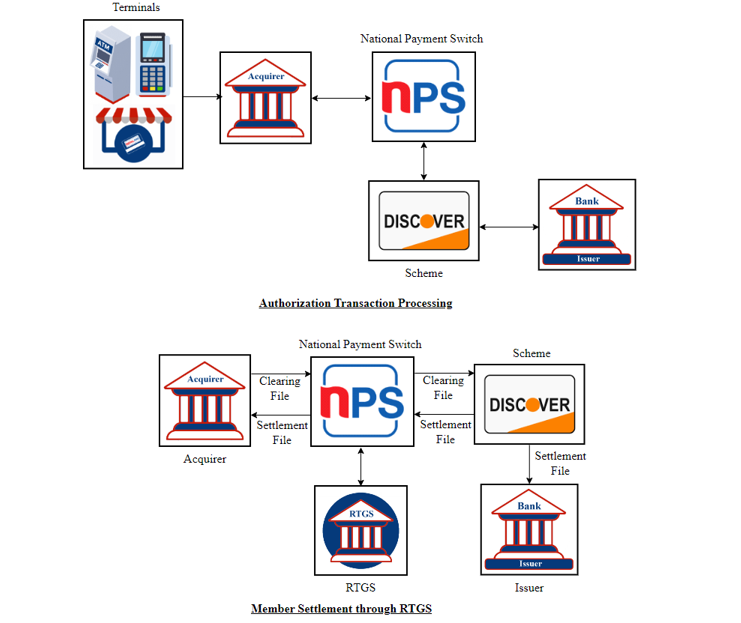
Figure 3: DMS Transaction Flow of International Transactions